5 Mile Outfall Diversion Plan Information
The City of Los Angeles will divert the Hyperion Water Reclamation Plant's effluent from its 5-mile outfall to its auxiliary 1-mile outfall. The diversion will occur from September 21 - October 26, 2015. Effluent will be switched from the 5-mile outfall to the 1-mile outfall with an average of 230 million gallons per day (mgd) over this 5 week period.
- LA Sanitation's (LASAN) Environmental Monitoring Division has developed an enhanced and comprehensive effluent and receiving water monitoring plan.
- The monitoring plan is in compliance with the Regional Water Quality Control Board and the Environmental Protection Agency permit requirements and will provide an assessment of environmental impacts.
Diversion Monitoring Plan
Effluent Monitoring
- Chronic Toxicity Testing (most sensitive species, red abalone) - once per week
- Conventional Chemistry/Instrumental Chemistry - 97 compounds/parameters. Sampling frequency range daily to once per month during the diversion.
Shoreline Monitoring
- Total Chlorine Residual (TCR)- Tracks the plume and measures disinfection dosage and exposure time effectiveness.
- Microbiology- Measures fecal indicator bacteria for human health risk (safe to swim) and to determine the effectiveness of the disinfection process.
Nearshore/Offshore Monitoring
- Total Chlorine Residual (TCR)- Tracks the plume and measures disinfection dosage and exposure time effectiveness.
- Microbiology- Measures fecal indicator bacteria for human health risk (safe to swim) and to determine the effectiveness of the disinfection process.
- Nutrients-Measures concentrations of multiple nutrient compounds for phytoplankton community change implications.
- Phytoplankton (Harmful Algal Blooms)- Investigate community composition changes resulting from increased nutrients into the nearshore environment.
- Benthic Macrofauna/Sediment Chemistry- Assess the toxicity of sediments near outfall as a result of the diversion.
Assets
- High-Frequency Radar (HFR) UCSD/SIO/SCCOOS - Estimates near real-time surface current water trajectories using Lagrangian particle tracking algorithm applied to HFR surface current velocity (speed and direction) vectors.
- Space-based Vehicles (Satellites) NASA/JPL - Intermittent data acquisition from a variety of satellite vehicles and sensors (e.g., Synthetic Aperture Radar) to hindcast plume magnitude and location.
- Current Drifters UCSB- GPS-equipped, dragged floats that provide real-time surface current velocities during both pre-diversion and diversion periods.
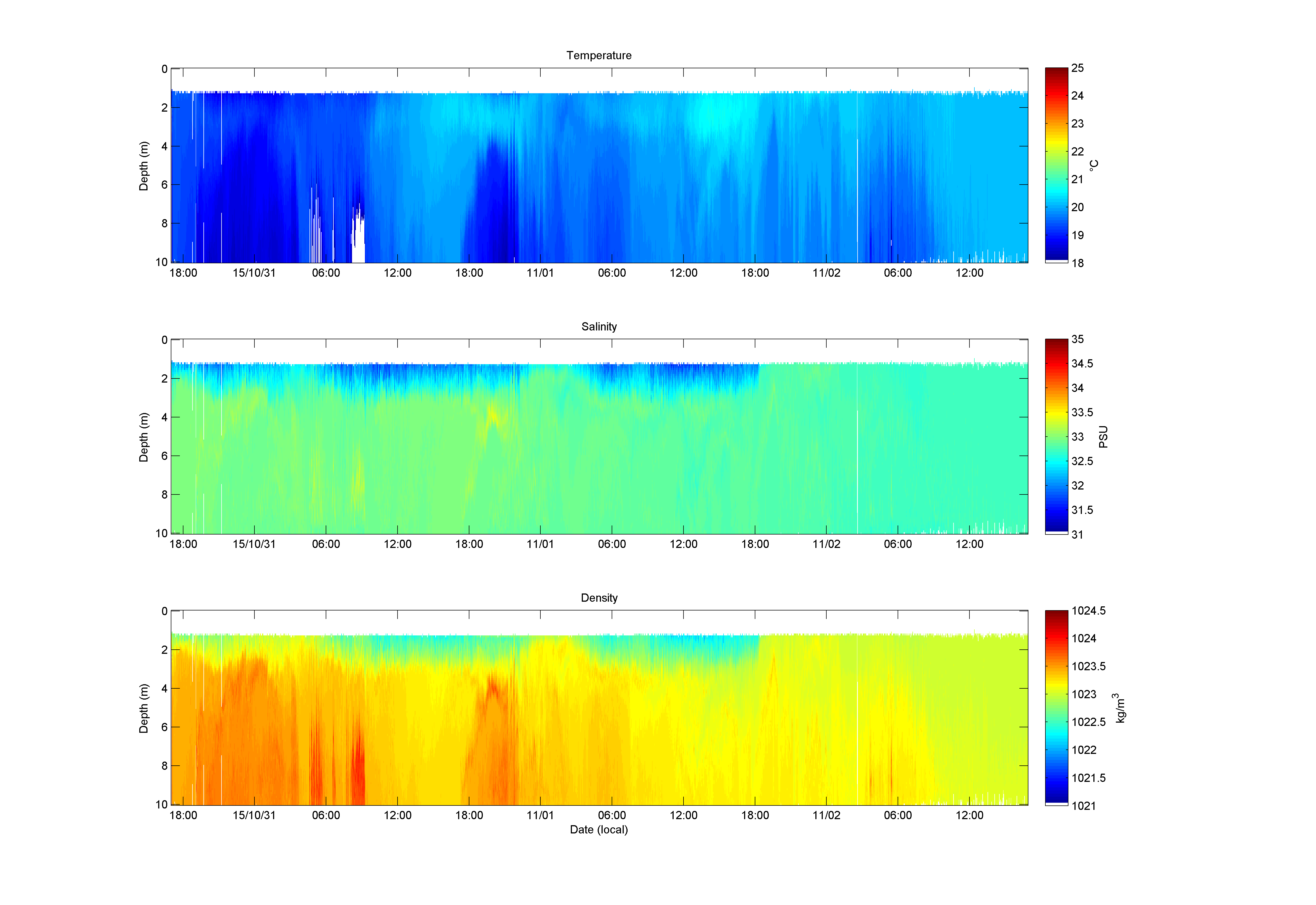
- Wirewalker UCSD/SIO - Continuous, wave-powered vertical profiler with CTD (conductivity-temperature-depth)to measure vertical location and thickness of the plume at the outfall in a mooring configuration.
- Continuous Surface Mapping CLAEMD - Tracks and delineates the plume (2D) with multiple water quality parameters using a YSI 6600 V2 data sonde (or probe) and a flow-through system.
- Profiling CTD CLAEMD - Multiple parameter instrument package for vertical profiling to track and delineate the plume (3D) with sensors for salinity, temperature, pressure (depth), colored dissolved organic matter (CDOM), chlorophyll-a, transmissivity (turbidity/water clarity), pH and dissolved oxygen.
- Website UCSD/SIO/SCCOOS - Project information portal for public, scientists, managers and regulators with near real-time data posting and a secure data upload.
Satellite: October 29, 2015
Aqua-MODIS Chlorophyll-a (chl-a), remote sensing reflectance at 555 nm (Rrs) and sea surface temperature (SST) from Oct. 29, 2015 at 14:41:55 PDT, during the diversion. An area of high chl-a is seen north of the outfall pipes and along the coast of Santa Monica Bay. There is also a smaller bloom circulating off the tip of San Pedro. These high signatures are also seen in the Rrs image at the 555 nm wavelength. These areas are also correlated with regions of cooler SST.